The Complete Swing Trading Guide for Beginners: Master 3 Proven Strategies
Reading Time: 18 minutes
Are you ready to discover a trading approach that doesn’t require staring at charts all day? Swing trading might be your perfect entry point into the stock market. This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about swing trading, from fundamental concepts to three powerful strategies that can help you capture profitable price movements.
What is Swing Trading? A Beginner’s Introduction
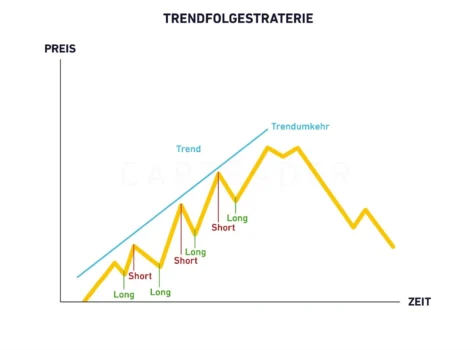
Swing trading is a strategic approach to stock trading that focuses on capturing short to medium-term price movements, typically lasting from a few days to several weeks. Think of it as riding the natural “swings” in stock prices – buying at the lows and selling at the highs.
Unlike day trading, which requires constant monitoring and quick decisions, swing trading offers a more relaxed pace that fits well with busy lifestyles. You’re not trying to catch every small price movement; instead, you’re positioning yourself to profit from the bigger waves in the market.
How Swing Trading Works
Stock prices rarely move in straight lines. Instead, they create patterns of higher highs and higher lows in uptrends, or lower highs and lower lows in downtrends. Swing traders capitalize on these predictable patterns by:
- Identifying trends using technical analysis
- Buying at swing lows in uptrending stocks
- Selling at swing highs to capture profits
- Holding positions for days or weeks rather than minutes or hours
Why Swing Trading Appeals to Beginners
1. Time Flexibility
You don’t need to quit your day job or monitor charts constantly. A few minutes of analysis in the evening can be sufficient to manage your swing trades.
2. Lower Stress Levels
Without the pressure of making split-second decisions, you can think more clearly about your trading choices and avoid emotional mistakes.
3. Better Risk Management
Longer holding periods allow you to set proper stop-losses and let profitable trades develop without premature exits.
4. Learning Opportunity
The slower pace gives you time to study market behavior and improve your technical analysis skills.
Essential Swing Trading Principles
Before diving into specific strategies, let’s establish the fundamental principles that separate successful swing traders from the rest:
The Do’s of Swing Trading
✅ Develop a Clear Trading Plan Define your entry and exit criteria before placing any trade. Know exactly why you’re buying a stock and when you’ll sell it.
✅ Use Proper Risk Management Never risk more than 1-2% of your trading capital on a single trade. This ensures you can survive losing streaks.
✅ Focus on Quality Over Quantity It’s better to make a few high-probability trades than to chase every possible opportunity.
✅ Keep a Trading Journal Document your trades, including your reasoning and emotions. This becomes invaluable for improving your strategy.
✅ Stay Disciplined Stick to your plan even when emotions try to override logic. Consistency is key to long-term success.
The Don’ts of Swing Trading
❌ Don’t Trade Without a Plan Entering trades based on gut feelings or tips from others is a recipe for disaster.
❌ Don’t Risk Too Much Overleveraging or risking large percentages of your capital will eventually lead to significant losses.
❌ Don’t Ignore Market Conditions Even the best strategies can fail in extremely volatile or trending markets. Adapt your approach accordingly.
❌ Don’t Let Emotions Drive Decisions Fear and greed are the swing trader’s worst enemies. Make decisions based on analysis, not feelings.
Strategy #1: Breakout Trading – Catching Momentum
Breakout trading is one of the most popular swing trading strategies because it’s relatively straightforward to understand and implement. This strategy focuses on identifying stocks that are breaking out of established price ranges or chart patterns.
How Breakout Trading Works
Key Concepts:
- Support and Resistance: Price levels where stocks tend to bounce or reverse
- Consolidation: Periods where stocks trade within a narrow range
- Volume Confirmation: Increased trading volume validates breakout signals
The Setup:
- Identify stocks trading in a clear range or pattern
- Wait for price to break above resistance (for long trades) or below support (for short trades)
- Confirm the breakout with increased volume
- Enter the trade as the breakout occurs
- Set stop-losses below the breakout level
Practical Example
Consider a stock that has been trading between $45 and $50 for several weeks. When the price breaks above $50 with high volume, it signals that buyers are taking control, potentially leading to further upward movement.
Entry Point: $50.10 (just above the breakout level) Stop Loss: $49.50 (below the previous resistance) Target: $55 (next resistance level or 10% gain)
Advantages of Breakout Trading
- Clear entry and exit signals
- Works well in trending markets
- Can capture significant moves early
- Relatively easy to automate
Limitations
- False breakouts can lead to losses
- Requires quick action when signals appear
- May not work well in choppy markets
Strategy #2: Moving Average Crossover – Riding the Trend
Moving averages are among the most widely used technical indicators in swing trading. They help smooth out price action and identify trend direction, making them perfect for beginner traders.
Understanding Simple Moving Averages (SMA)
A Simple Moving Average calculates the average closing price over a specific number of periods. Common timeframes include:
- 20-day SMA: Short-term trend indicator
- 50-day SMA: Medium-term trend indicator
- 200-day SMA: Long-term trend indicator
The Golden Cross and Death Cross
Golden Cross: When a shorter-term moving average crosses above a longer-term moving average, signaling a potential uptrend.
Death Cross: When a shorter-term moving average crosses below a longer-term moving average, signaling a potential downtrend.
Trading the Strategy
For Bullish Trades:
- Wait for the 20-day SMA to cross above the 50-day SMA
- Confirm that the stock price is above both moving averages
- Enter the trade when price breaks above the recent swing high
- Set stop-loss below the longer-term moving average
- Hold until the moving averages cross back or target is reached
For Bearish Trades:
- Wait for the 20-day SMA to cross below the 50-day SMA
- Confirm that the stock price is below both moving averages
- Enter the trade when price breaks below the recent swing low
- Set stop-loss above the longer-term moving average
- Hold until the moving averages cross back or target is reached
Advantages of Moving Average Strategy
- Easy to understand and implement
- Works well in trending markets
- Provides clear trend direction
- Reduces emotional decision-making
Limitations
- Lagging indicator (signals come after moves begin)
- Can generate false signals in sideways markets
- May miss the beginning of strong trends
Strategy #3: MACD Trading – Momentum and Trend Combined
The Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) is a versatile indicator that combines trend-following and momentum characteristics, making it excellent for swing trading.
Understanding MACD Components
MACD Line: The difference between the 12-period EMA and 26-period EMA Signal Line: A 9-period EMA of the MACD line Histogram: The difference between the MACD line and signal line Zero Line: The neutral point where momentum is balanced
MACD Trading Signals
Bullish Signals:
- MACD line crosses above the signal line
- MACD histogram turns positive
- MACD line crosses above the zero line
Bearish Signals:
- MACD line crosses below the signal line
- MACD histogram turns negative
- MACD line crosses below the zero line
Trading the MACD Strategy
Entry Rules:
- Wait for MACD line to cross above signal line (bullish) or below (bearish)
- Confirm the signal with histogram movement in the same direction
- Look for additional confirmation from price action (breakouts, support/resistance)
- Enter the trade when all conditions align
Exit Rules:
- Exit when MACD lines cross back in the opposite direction
- Take profits at predetermined targets
- Use stop-losses to limit downside risk
Enhancing MACD Signals
To improve the reliability of MACD signals, consider combining them with:
- Price action: Look for breakouts or bounces from support/resistance
- Volume analysis: Confirm signals with increased trading volume
- Multiple timeframes: Use higher timeframes for trend direction
- Other indicators: Combine with RSI or moving averages for additional confirmation
Risk Management: Protecting Your Capital
Successful swing trading isn’t just about finding good entry points – it’s about managing risk effectively to preserve your capital for future opportunities.
Position Sizing
Never risk more than 1-2% of your total trading capital on any single trade. This rule ensures you can survive a series of losing trades without significant damage to your account.
Example:
- Trading account: $10,000
- Maximum risk per trade: $200 (2%)
- If stop-loss is $2 per share, maximum position size: 100 shares
Stop-Loss Orders
Always use stop-loss orders to limit potential losses. Place them at logical levels based on:
- Technical support/resistance levels
- Below/above moving averages
- Percentage-based stops (5-10% from entry)
Take-Profit Targets
Set realistic profit targets based on:
- Technical resistance levels
- Risk-reward ratios (aim for 2:1 or better)
- Average true range of the stock
- Overall market conditions
Managing Volatility
Market volatility can significantly impact swing trading performance. Here’s how to adapt:
During High Volatility:
- Reduce position sizes
- Use wider stop-losses
- Consider shorter holding periods
- Avoid trading around earnings announcements
During Low Volatility:
- Look for range-bound trading opportunities
- Use tighter stop-losses
- Consider longer holding periods
- Focus on breakout setups
Building Your Swing Trading Plan
Step 1: Education and Preparation
Before risking real money, invest time in learning:
- Technical analysis basics
- Chart pattern recognition
- Risk management principles
- Market psychology
Step 2: Define Your Strategy
Choose one of the three strategies outlined above and thoroughly understand:
- Entry criteria
- Exit rules
- Risk management parameters
- Market conditions where it works best
Step 3: Paper Trading
Practice your strategy with simulated trades before using real money. This helps you:
- Gain confidence in your approach
- Identify weaknesses in your plan
- Develop emotional discipline
- Refine your execution
Step 4: Start Small
When you’re ready to trade with real money:
- Start with small position sizes
- Focus on high-probability setups
- Keep detailed records of your trades
- Gradually increase size as you gain experience
Step 5: Continuous Improvement
Successful swing trading is an ongoing learning process:
- Review your trades regularly
- Identify patterns in your wins and losses
- Adjust your strategy based on market conditions
- Stay updated on market developments
Common Swing Trading Mistakes to Avoid
1. Overtrading
Many beginners try to trade too frequently, leading to increased costs and emotional fatigue. Focus on quality setups rather than quantity.
2. Ignoring Risk Management
Some traders get caught up in the excitement of profits and forget to manage risk properly. Always use stop-losses and position sizing.
3. Emotional Trading
Letting fear and greed drive decisions is a sure way to lose money. Stick to your plan regardless of emotions.
4. Lack of Patience
Swing trading requires patience to wait for the right setups and let profits develop. Don’t rush into trades.
5. No Trading Plan
Trading without a clear plan is like driving without a destination. Always know why you’re entering a trade and when you’ll exit.
Tools and Resources for Swing Trading
Essential Technical Analysis Tools
- Charting platforms: TradingView, MetaTrader, or broker-provided charts
- Screening tools: For finding stocks that meet your criteria
- News services: Stay informed about market developments
- Economic calendars: Track important announcements
Key Metrics to Monitor
- Relative Strength Index (RSI): Measures overbought/oversold conditions
- Volume: Confirms price movements
- Average True Range (ATR): Helps set stop-losses
- Beta: Measures stock volatility relative to the market
Is Swing Trading Right for You?
Consider swing trading if you:
- Have limited time for active trading
- Prefer less stressful trading approaches
- Want to learn technical analysis
- Can handle holding positions overnight
- Have patience for setups to develop
Swing trading might not be suitable if you:
- Need immediate gratification
- Cannot handle overnight risk
- Prefer fundamental analysis
- Want to trade full-time immediately
- Have very limited capital
The Path Forward
Swing trading offers an excellent balance between active trading and long-term investing. It provides enough action to keep you engaged while allowing time for proper analysis and decision-making.
Remember, successful swing trading is not about finding the perfect strategy – it’s about finding a strategy that fits your personality, risk tolerance, and lifestyle, then executing it consistently with proper risk management.
Start with one of the three strategies outlined in this guide, practice with paper trading, and gradually develop your skills. With patience, discipline, and continuous learning, swing trading can become a valuable addition to your investment approach.
The key to success lies not in complex strategies or secret indicators, but in understanding market behavior, managing risk effectively, and maintaining the discipline to stick to your plan even when emotions try to interfere.
Begin your swing trading journey today, but remember: education and preparation are your best investments. Take the time to learn properly, and the profits will follow.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How much money do I need to start swing trading? A: While there’s no minimum, having at least $5,000-$10,000 allows for proper diversification and risk management. Start with paper trading if you have less capital.
Q: Can I swing trade with a full-time job? A: Yes! Swing trading is ideal for people with full-time jobs since it doesn’t require constant monitoring. Spend 15-30 minutes each evening analyzing your positions.
Q: How many stocks should I trade at once? A: Beginners should start with 3-5 positions to maintain proper oversight. As you gain experience, you can gradually increase this number.
Q: What’s the difference between swing trading and day trading? A: Day trading involves buying and selling within the same day, while swing trading holds positions for days to weeks. Swing trading is generally less stressful and requires less time commitment.
Q: How do I know when to exit a profitable trade? A: Set profit targets based on technical analysis before entering the trade. Consider taking partial profits at key resistance levels and letting the rest run with a trailing stop-loss.
Ready to start your swing trading journey? Remember, success comes from consistent application of proven strategies combined with disciplined risk management. Start small, learn continuously, and let your skills develop over time.